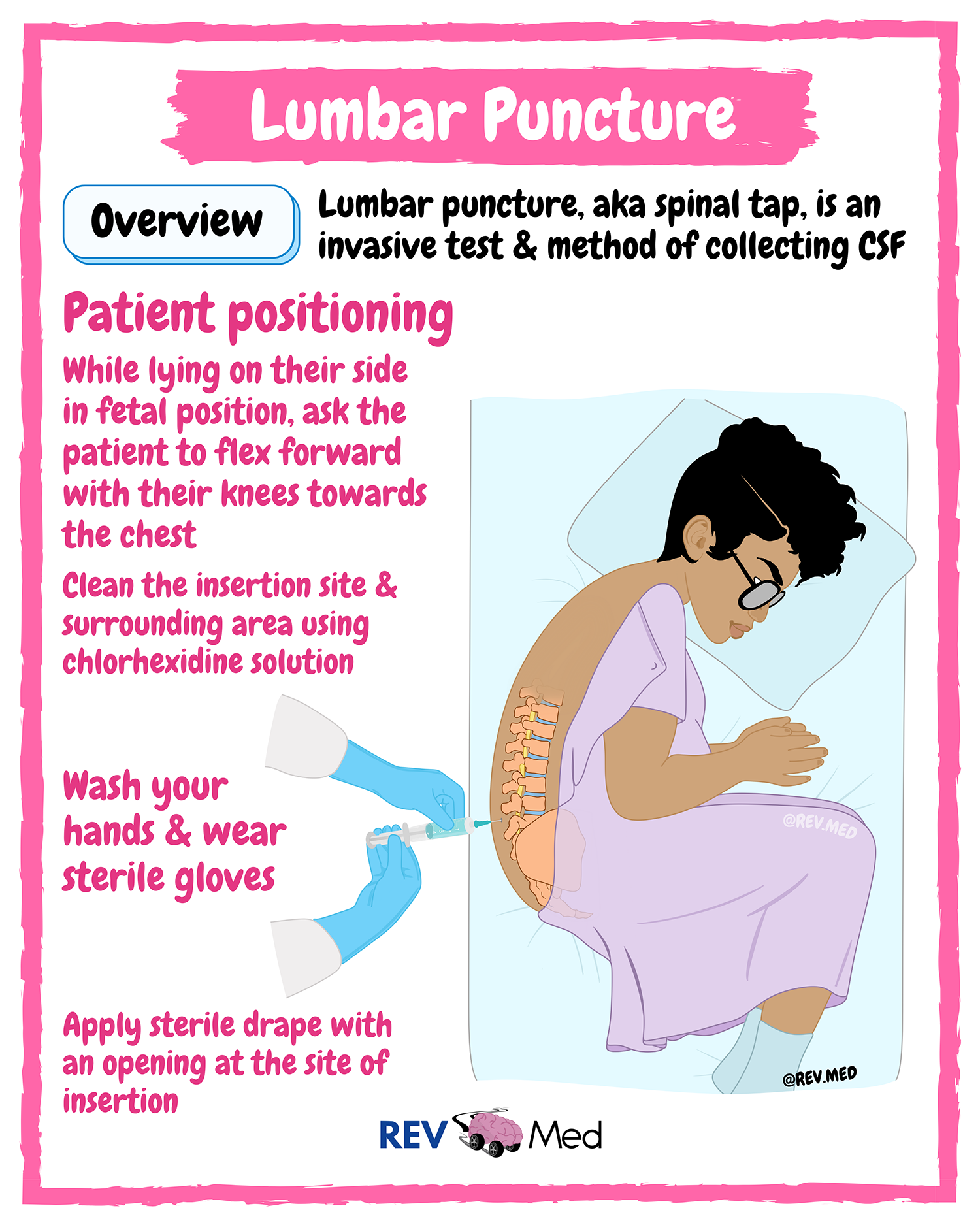
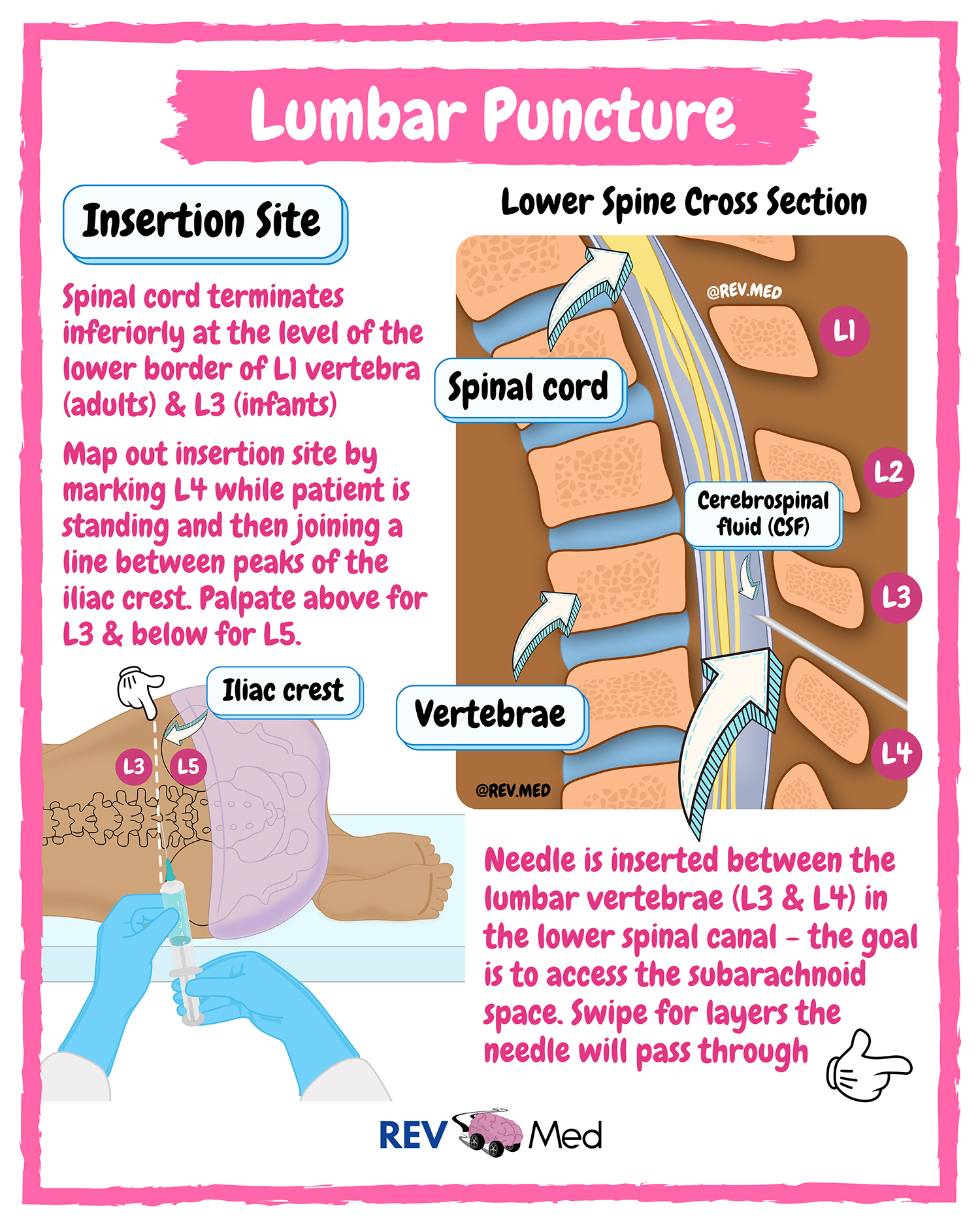
A lumbar punctureA procedure where a needle is placed in the lower part of the spine (the lumbar spine) to access cerebrospinal fluid. Click the term to read more (LP) is an invasive procedure. It is part of an extensive workup when a neurological disorder is suspected. Also known as a spinal tapA procedure where a needle is placed in the lower part of the spine (the lumbar spine) to access cerebrospinal fluid. Click the term to read more, an LP can detect if an infection, bleeding, or an abnormal process (ie: cancer) is occurring in the central nervous system. As part of the Dandy CriteriaCriteria used for diagnosing patients with IIH. Click the term to read more, the information obtained from an LP is essential to make the diagnosis of IIH and in ruling out another cause that can be treated in another manner. Throughout the course of IIH, it may be necessary to repeat an LP several times to alleviate the high pressure in the brain.
Reasons to perform (indications) or not perform (contraindications) a lumbar puncture:

A lumbar puncture is an invasiveinvolving the introduction of instruments or other objects into the body Click the term to read more procedure used for diagnostic and therapeutic purposes. It is diagnostic because it can measure pressure in the brain (opening pressure) and the cerebrospinal fluidFluid that is made by specialized cells in the ventricles of the brain. Click the term to read more obtained can be analyzed for appearance, and red blood cells, white blood cells, protein, and glucose can be quantified. The results of the CSFFluid that is made by specialized cells in the ventricles of the brain. Click the term to read more fluid can detect if there is a viral or bacterial infection and diagnose some autoimmune disorders.
| CSF Fluid | Normal | Viral | Bacterial |
| Opening Pressure | 5-20 cm H₂0 | Normal or elevated | Elevated |
| Appearance | Clear | Clear | Turbid |
| WBC | < 5 and no PMNs* | 10-1000 | > 100 and > 80% PMNs* |
| RBC | < 10 | Normal (< 10) | Normal (< 10) |
| Protein | 15-45 mg/dL | Elevated >50 mg/dL | Elevated > 50 mg/dL |
| Glucose | > 60% serum glucose | < 40% serum glucose | > 60% serum glucose |
A lumbar puncture is also therapeutic as it helps decrease the pressure in the brain. This is a critical intervention used for idiopathicThe term idiopathic is used when there is no detectable reason for something. Click the term to read more intracranial hypertension (IIH), if increased pressure from CSF fluid is causing papilledemaSwelling of the optic nerve that carries visual signals from the eye to the brain. Click the term to read more leading to vision loss, debilitating headaches, and a wide range of chronic symptoms. Having CSF removed can help bring the pressure in the brain back to normal and can reverse some of the known signs and symptoms of IIH. It can be performed in an emergent or non-emergent setting depending on symptoms and physical exam findings.