Many have acknowledged that the word obesity as a medical term is outdated. Some organizations have proposed using an alternate word to characterize the physiological impact that occurs to the body with varying degrees of adipose tissue.
The origin of the word obese derives from the Latin word obesitas meaning “fatness” or “corpulence”. During the middle ages, when someone was overweight it was looked at positively as a sign of wealth. Nowadays, the word obese is associated with negative and dangerous terms like lazy, non motivated and slow.
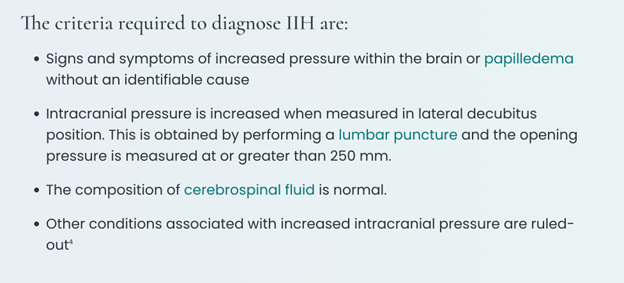
The medical diagnosis pseudotumor cerebri was first described in the 1800s as “neurological findings without an anatomical cause”. Over the course of 200 years, the definition and management has not significantly changed.
IdiopathicThe term idiopathic is used when there is no detectable reason for something. Click the term to read more intracranial hypertension (IIH) is a neurological condition with its own criteria, including having an elevated BMIA value derived from the mass (weight) and height of a person. A healthy range is between 18.5-24.9, overweight is defined as 25-29.9 and obese… Click the term to read more to make the diagnosis. Today, we know that IIH includes a spectrum of symptoms and findings and can affect those with any BMI. These people may not meet the Dandy Criteria but may improve with the same treatment.
The body mass indexA value derived from the mass (weight) and height of a person. A healthy range is between 18.5-24.9, overweight is defined as 25-29.9 and obese… Click the term to read more (BMI) is a tool utilized by the medical world to determine if someone is under, normal, overweight, or obese. Unfortunately the BMI equation has a lot of pitfalls, it does not account for muscle mass, ethnicity, gender, and fat distribution.1
Dr. Sofia Cienfuegos discussed in her webinar, The Impact on Weight Bias in Obesity and IIH, that weight stigma is defined as “The discriminatory acts and ideologies targeted towards individuals because of their weight and size.” This bias can lead to stereotyping and beliefs that are harmful in the care of patients who are overweight or obese.
In 2017 the American Association for Clinical Endocrinology (AACE) introduced the nomenclature adiposity-based chronic disease (ABCD) to acknowledge that this condition is not solely weight-based but an entity that includes body fat distribution in association with chronic illnesses. It also includes an initiative to improve health through prevention.2

There is no singular test that will determine if someone is overweight or at a weight that increases the chances of systemic diseases. Individually, each test used to determine adiposity has its own pros and cons.
A comprehensive workup can assist in targeting potential causes for higher than normal adiposity:
- Performing a full history and physical exam.
- Physical testing such as a BMI, or waist-to-hip ratio, skinfold thickness, DEXA scan, bioelectric impedance, etc.
- Blood work that can include assessing the pancreas, kidney, liver, hormone levels, vitamin and micronutrient levels.
The above information can provide an objective determination of overall health. As the reasons for uncontrolled weight gain are innumerable, it is helpful to identify causes that are modifiable such as nonproductive lifestyle choices.
A referral to an endocrinologist, who is trained in hormones and metabolism can dive deeper into complex cases. A nutritionist or licensed dietician can dedicate time to identify personalized nutritional goals.
The approach to each person should be individualized and carefully assessed. If one is failing at weight loss due to traditional methods such as diet and exercise, it is time to look at other reasons like hormonal imbalances and organ dysfunction. Understanding the concept of adiposity-based chronic disease (ABCD), could shed some insight.



