What are GLP-1 RAs? And what role do they play in the management of idiopathicThe term idiopathic is used when there is no detectable reason for something. Click the term to read more intracranial hypertension (IIH)?
GLP-1 RAglucagon-like peptide receptor agonists Click the term to read more stands for glucagon-like peptide receptor agonists. This class of medication is receiving a lot of attention at the moment because the list of medical conditions it can treat is soaring.
GLP-1 is a naturally occurring hormone made in the intestine. GLP-1 RAs are the synthetic version of GLP-1.
The 4 main functions of the GLP-1 hormone is to:
- Stimulate insulin secretion (regulating blood sugar from the pancreas)
- Inhibit glucagon secretion (regulating blood sugar from the liver)
- Decrease intestinal motility (feeling full with less intake)
- Reduce appetite (tells your brain you are not hungry)
GLP-1 RAs have been on the market since 2005, initially indicated to treat type-2 diabetes mellitus. Because of its success in reversing diabetic complications and achieving weight loss, the indications for use expanded to treat people with a BMIA value derived from the mass (weight) and height of a person. A healthy range is between 18.5-24.9, overweight is defined as 25-29.9 and obese… Click the term to read more of over 30 or a BMI between 27 and 30 with a high risk condition like a cardiovascular event or high lipids to aid in achieving weight loss. With weight loss, many chronic conditions are reversed or prevented like strokes, heart attacks, and fatty liver disease.
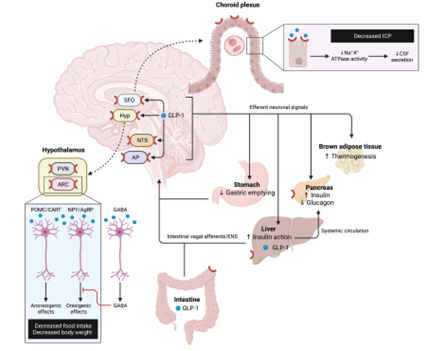
A portion of patients fit the criteria of having a BMI of over 30 as the primary cause of IIH. In these patients, if one loses more than 10% of their weight, IIH symptoms can improve or resolve. GLP-1 RAs can cross the blood brain barrier so they also can decrease ICPincreased intracranial pressure Click the term to read more, preventing the cascade of events that occurs in IIH.